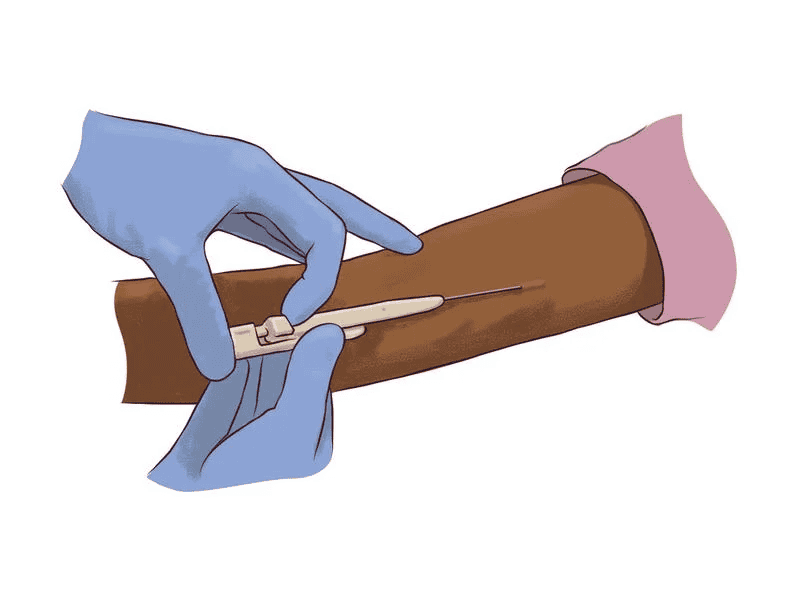
Nexplanon is primarily used as a contraceptive method to prevent pregnancy. It is a long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) method, which means once it’s implanted, it can provide continuous pregnancy prevention for up to three years.
How it Works: Nexplanon works by releasing a progestin hormone called etonogestrel into the body. This hormone prevents pregnancy through several mechanisms, including:
- Inhibiting ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary).
- Thickening cervical mucus, which makes it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
- Thinning the lining of the uterus, which may prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Insertion: Nexplanon is inserted subdermally (under the skin) in the inner side of the upper arm by a healthcare provider. The insertion procedure is relatively quick and typically done under local anesthesia.
Duration of Effectiveness: Once inserted, Nexplanon provides effective contraception for up to three years. After three years, it should be removed and may be replaced with a new implant if continued contraception is desired.
Effectiveness: Nexplanon is highly effective in preventing pregnancy, with a success rate of over 99% when used correctly. It is one of the most reliable forms of contraception available.
Side Effects: While Nexplanon is generally safe and well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects. Common side effects may include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns (such as irregular bleeding, spotting, or absence of menstruation).
- Headache.
- Breast tenderness.
- Weight gain.
- Acne.
- Mood changes.
Serious side effects are rare but may include:
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus).
- Ovarian cysts.
- Blood clots.
Removal: Nexplanon should be removed by a healthcare provider at the end of its effective lifespan (after three years) or earlier if desired by the individual. The removal procedure is typically quick and straightforward.
Interactions: Nexplanon may interact with certain medications, including some antibiotics, anticonvulsants, antiretroviral drugs, and herbal supplements. It’s important to discuss any medications or supplements you’re taking with your healthcare provider before getting Nexplanon inserted.
Effect on Fertility: Fertility typically returns quickly after Nexplanon is removed. Most individuals can conceive shortly after removal if they desire to become pregnant.
Cost and Availability: Nexplanon is available by prescription and may be covered by insurance. The cost may vary depending on insurance coverage and healthcare provider.
Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Before deciding to use Nexplanon, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss whether it’s the right contraceptive option for you. Your healthcare provider can provide personalized advice based on your medical history, preferences, and individual needs.
How does Nexplanon work?
Nexplanon works primarily by releasing a synthetic hormone called etonogestrel into the body. Etonogestrel is a progestin, which is a synthetic version of the hormone progesterone.
Here’s how Nexplanon works to prevent pregnancy:
- Inhibition of Ovulation: One of the main mechanisms of Nexplanon is to suppress ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovary. By maintaining a steady level of progestin in the body, Nexplanon inhibits the hormonal signals necessary for the maturation and release of eggs from the ovaries. Without ovulation, there is no egg available for fertilization by sperm, thereby preventing pregnancy.
- Thickening of Cervical Mucus: Nexplanon causes changes in the cervical mucus, making it thicker and more viscous. This thickening effect creates a barrier that makes it difficult for sperm to penetrate the cervix and reach the egg, reducing the chances of fertilization.
- Changes in Uterine Lining: Nexplanon also causes thinning of the endometrial lining of the uterus. This thinning makes the uterine environment less suitable for the implantation of a fertilized egg, further reducing the likelihood of pregnancy.
By combining these three mechanisms—ovulation suppression, thickening of cervical mucus, and changes in the uterine lining—Nexplanon provides highly effective contraception, with a failure rate of less than 1% when used correctly. It offers women a reliable and long-lasting method of birth control, with the convenience of not needing to remember to take a daily pill or use other forms of contraception.
How is Nexplanon inserted?
Inserting Nexplanon is a straightforward procedure typically performed by a healthcare provider in an office setting. Before insertion, the healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment, including reviewing medical history and discussing contraceptive options and potential side effects. Here’s an overview of the Nexplanon insertion process:
First, the provider will clean and sterilize the insertion site, usually the inner side of the non-dominant upper arm, with an antiseptic solution. They will then use a local anesthetic to numb the area, ensuring minimal discomfort during the procedure.
Next, the healthcare provider will use a specialized applicator to insert the Nexplanon implant just beneath the skin. The implant is a small, flexible rod about the size of a matchstick, and the applicator is designed to quickly and accurately place it in the subdermal tissue.
Once inserted, the healthcare provider will verify the correct placement of the implant by palpating the area and ensuring that it can be felt just beneath the skin. They may also provide instructions on how to feel for the implant to ensure its presence over time.
After insertion, the healthcare provider will cover the insertion site with a small bandage to keep it clean and protected. They will also provide information on what to expect after insertion, including potential side effects and when to follow up for removal or additional care.
Overall, Nexplanon insertion is a relatively simple and safe procedure that offers women a convenient and effective long-term contraceptive option.
How long does Nexplanon last?
Nexplanon lasts for up to three years once it’s inserted. This means that once you have the Nexplanon implant placed under your skin, you can rely on it for contraception for a period of three years. After three years, the effectiveness of Nexplanon decreases, and it should be removed or replaced with a new implant if you wish to continue using it for birth control. It’s essential to keep track of the expiration date of your Nexplanon implant and discuss with your healthcare provider when it’s time for removal or replacement. By adhering to the recommended duration of use, you can ensure optimal contraceptive effectiveness and continue to benefit from the convenience and reliability of Nexplanon for preventing pregnancy.
Is Nexplanon effective?
Yes, Nexplanon is highly effective at preventing pregnancy when used correctly. It is one of the most reliable forms of contraception available, with a success rate of over 99%. This means that fewer than 1 out of 100 women using Nexplanon will become pregnant each year.
The effectiveness of Nexplanon is attributed to its mechanism of action, which involves the slow release of the progestin hormone etonogestrel into the body. Etonogestrel works by inhibiting ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary), thickening cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg, and thinning the lining of the uterus to prevent the implantation of a fertilized egg.
It’s important to note that while Nexplanon is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, no contraceptive method is 100% foolproof. Factors such as improper insertion, medication interactions, and rare device failures may affect its effectiveness. However, Nexplanon is considered one of the most reliable contraceptive options available and provides women with long-lasting and convenient birth control when used as directed.
What are the advantages of using Nexplanon?
Nexplanon offers several advantages for individuals seeking reliable contraception. Firstly, it boasts over 99% effectiveness, providing peace of mind against unintended pregnancy. Its long-lasting nature means up to three years of continuous contraception without daily maintenance. This convenience suits busy lifestyles and ensures privacy as it’s discreetly inserted under the skin. Additionally, Nexplanon’s reversibility allows for a swift return to fertility upon removal, accommodating changing family planning needs. With minimal discomfort during insertion and the potential for hormonal benefits like reduced menstrual bleeding, Nexplanon stands as a convenient, effective, and versatile contraceptive option for many.
What are the potential side effects of Nexplanon?
While Nexplanon is generally safe and well-tolerated, it may cause some side effects in some individuals. Common side effects may include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, such as irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, or absence of menstruation.
- Headaches.
- Breast tenderness.
- Weight gain.
- Acne.
- Mood changes.
These side effects typically improve over time as the body adjusts to the presence of the hormone in Nexplanon. However, some individuals may experience more severe or persistent side effects, including:
- Ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterus).
- Ovarian cysts.
- Blood clots.
It’s essential to discuss any concerns or unusual symptoms with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on managing side effects and determine if Nexplanon is the right contraceptive option for you.
Can Nexplanon cause weight gain?
Weight gain is listed as a potential side effect of Nexplanon, but it doesn’t affect everyone who uses it. Some individuals may experience weight changes while using Nexplanon, while others may not notice any difference in their weight.
The exact mechanism by which Nexplanon might cause weight gain is not fully understood, but it’s believed to be related to hormonal changes induced by the progestin hormone, etonogestrel, which is released by the implant. Progestins can sometimes lead to fluid retention or changes in appetite, both of which could contribute to weight gain in some individuals.
It’s important to note that weight gain associated with Nexplanon is typically modest and gradual. Additionally, not everyone who uses Nexplanon will experience this side effect, and individual responses may vary.
If you’re concerned about weight gain while using Nexplanon, it’s a good idea to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and help you explore alternative contraceptive options if necessary. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine can also help manage weight while using Nexplanon or any other form of contraception.
Can Nexplanon affect my menstrual cycle?
Yes, Nexplanon can affect menstrual bleeding patterns in individuals who use it. Changes in menstrual cycles are among the common side effects of Nexplanon.
Some individuals may experience:
- Irregular bleeding: This can manifest as unpredictable episodes of bleeding or spotting throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Prolonged bleeding: Some individuals may experience longer or heavier menstrual periods than usual.
- Absence of menstruation: Others may experience amenorrhea, which is the absence of menstrual periods. This occurs in some users and is not a cause for concern, as Nexplanon can alter the hormonal balance that regulates menstruation.
It’s essential to understand that these changes are generally not harmful and often improve over time as the body adjusts to the hormone released by Nexplanon. However, if you experience severe or persistent changes in your menstrual cycle or have concerns, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance, address any concerns, and monitor your condition if needed.
How soon does Nexplanon start working after insertion?
Nexplanon starts working quickly after insertion, but it’s essential to wait for a certain period before relying on it solely for contraception. For individuals who have Nexplanon inserted within the first five days of their menstrual cycle, it starts working immediately, providing immediate contraceptive protection against pregnancy. However, for those who have Nexplanon inserted at any other time during their menstrual cycle, it’s recommended to use a backup method of contraception, such as condoms, for the first seven days after insertion. This ensures adequate time for Nexplanon to become effective in preventing pregnancy. After this initial period, Nexplanon provides continuous contraceptive protection for up to three years, making it a reliable and convenient birth control option for many individuals.
Can I feel Nexplanon once it’s inserted?
Typically, you should not be able to feel Nexplanon once it’s properly inserted. The implant is a small, flexible rod about the size of a matchstick that is placed just under the skin of your upper arm. It’s positioned subdermally, meaning it’s inserted beneath the skin’s surface.
After insertion, your healthcare provider will confirm the placement of Nexplanon by palpating the area to ensure that it can be felt just beneath the skin. They will also provide instructions on how to check for the presence of the implant periodically to ensure it remains in place.
In rare cases, some individuals may be able to feel the implant if it shifts slightly or if there is swelling or inflammation at the insertion site. If you experience any discomfort, unusual sensations, or concerns about the placement of Nexplanon, it’s essential to contact your healthcare provider promptly for further evaluation.
How is Nexplanon removed?
Nexplanon removal is a relatively simple and quick procedure that should be performed by a trained healthcare provider. Here’s an overview of the removal process:
- Preparation: Before removal, your healthcare provider will review your medical history and discuss any concerns or reasons for wanting to remove Nexplanon. They will also explain the procedure and address any questions you may have.
- Locating the Implant: Your healthcare provider will locate the Nexplanon implant by palpating the area of your upper arm where it was inserted. The implant can usually be felt just beneath the skin.
- Anesthesia: To minimize discomfort, your healthcare provider may inject a local anesthetic into the area around the implant insertion site. This numbs the area and reduces pain during the removal procedure.
- Incision: Once the area is numb, your healthcare provider will make a small incision (usually about 2-3 mm) over the end of the implant. This incision allows them to access the implant for removal.
- Removal: Using special instruments, your healthcare provider will grasp the end of the implant and gently slide it out through the incision. The removal process is typically quick and should not cause significant discomfort.
- Closure: After the implant is removed, your healthcare provider will close the incision with adhesive strips or sutures, if necessary. They may also apply a sterile bandage to the site to protect it as it heals.
- Aftercare: Your healthcare provider will provide instructions on caring for the removal site, including keeping it clean and dry and avoiding strenuous activities for a short period. They will also discuss any follow-up care or contraceptive options if needed.
It’s important to have Nexplanon removed by a healthcare provider to ensure safe and proper extraction of the implant. Attempting to remove Nexplanon on your own or by someone who is not trained to do so can lead to complications or injury. If you have any concerns about Nexplanon removal or need assistance, be sure to contact your healthcare provider for guidance.
Can Nexplanon be used while breastfeeding?
Yes, Nexplanon can generally be used while breastfeeding, and it’s considered a suitable contraceptive option for breastfeeding individuals. Since Nexplanon contains only the progestin hormone etonogestrel and does not contain estrogen, it is unlikely to affect breast milk production or the health of the breastfeeding infant.
However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any form of contraception while breastfeeding. Your healthcare provider can evaluate your individual circumstances, medical history, and breastfeeding goals to determine the most appropriate contraceptive option for you.
Additionally, while Nexplanon is generally safe for use during breastfeeding, it’s important to be aware that small amounts of progestin may pass into breast milk. Although these amounts are usually too low to be harmful to the infant, some healthcare providers may recommend waiting until breastfeeding is well-established before starting Nexplanon to minimize any potential impact on milk supply.
Overall, Nexplanon can be a convenient and effective contraceptive option for individuals who are breastfeeding, but it’s essential to discuss your options with your healthcare provider to ensure that you choose the method that best meets your needs and preferences.
Can Nexplanon protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
No, Nexplanon does not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Nexplanon is a hormonal contraceptive method that prevents pregnancy by releasing the progestin hormone etonogestrel into the body. While it is highly effective at preventing pregnancy, it does not provide any protection against STIs, such as HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea, chlamydia, or syphilis.
To reduce the risk of contracting STIs, individuals should use barrier methods of contraception, such as condoms, during sexual activity. Condoms provide a physical barrier that helps prevent the exchange of bodily fluids, which can transmit STIs.
It’s essential to use both contraception and barrier methods consistently and correctly to protect against both pregnancy and STIs. Additionally, individuals who are sexually active should consider regular STI testing and communicate openly with their partners about sexual health and protection.
Can Nexplanon be used as emergency contraception?
No, Nexplanon cannot be used as emergency contraception.
Emergency contraception is a form of contraception used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex, such as a condom breaking or forgetting to take birth control pills. Nexplanon, on the other hand, is a long-acting contraceptive method that is inserted under the skin and provides continuous contraception for up to three years.
Emergency contraception options include dedicated emergency contraceptive pills, copper intrauterine devices (IUDs), or certain types of regular birth control pills taken in higher doses.
It’s important to note that emergency contraception should be used as soon as possible after unprotected sex, ideally within 72 hours, to be most effective. If you are considering emergency contraception, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can provide guidance on the most appropriate option for your individual circumstances.
Can Nexplanon affect my mood?
Yes, Nexplanon can potentially affect mood in some individuals. Mood changes are listed as a possible side effect of Nexplanon use, although they do not occur in everyone who uses the contraceptive implant.
Some individuals may experience:
- Mood swings
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Emotional changes
These mood changes may be related to the hormonal effects of Nexplanon, particularly the progestin hormone etonogestrel released by the implant. Hormonal fluctuations can sometimes impact mood regulation and emotional well-being in some individuals.
If you notice significant changes in mood or emotional well-being while using Nexplanon, it’s essential to discuss these symptoms with your healthcare provider. They can help assess whether the mood changes are related to Nexplanon or other factors, such as underlying mental health conditions, stress, or lifestyle factors. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend adjustments to your contraceptive regimen or other interventions to address mood changes effectively.
Can Nexplanon be used by women with certain medical conditions?
Nexplanon may not be suitable for use by women with certain medical conditions or risk factors. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting Nexplanon or any other form of contraception, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or specific health concerns. Your healthcare provider can help determine whether Nexplanon is safe and appropriate for you based on your medical history, current health status, and individual risk factors.
Some medical conditions or factors that may influence the suitability of Nexplanon include:
- History of blood clots or thromboembolic disorders
- Liver disease or impaired liver function
- History of breast cancer or other hormone-sensitive cancers
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding or abnormal uterine bleeding
- Severe obesity
- Diabetes mellitus with vascular disease
- Active or recent history of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack or stroke
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- History of migraines with aura
- Gallbladder disease
Additionally, certain medications or treatments may interact with Nexplanon and affect its effectiveness or safety. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking before starting Nexplanon.
Your healthcare provider can assess your individual health status and medical history to determine whether Nexplanon is a suitable contraceptive option for you. They can also discuss alternative contraceptive methods or additional precautions if Nexplanon is not recommended based on your specific circumstances.
Can Nexplanon be used by women of all ages?
Nexplanon is generally suitable for use by women of reproductive age, including adolescents and adults. However, the suitability of Nexplanon may depend on various factors, including individual health status, medical history, and personal preferences.
While Nexplanon is a highly effective contraceptive option, it’s essential for women of all ages to discuss their contraceptive needs and preferences with a healthcare provider before starting Nexplanon or any other form of contraception. Healthcare providers can help assess whether Nexplanon is the right choice based on factors such as:
- Age: Nexplanon is suitable for women of reproductive age, including adolescents who have reached puberty and adults of all ages.
- Medical history: Certain medical conditions or risk factors may influence the suitability of Nexplanon. It’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns you may have.
- Reproductive goals: Nexplanon provides long-term contraception for up to three years. Women should consider their reproductive goals and plans for the future when choosing a contraceptive method.
- Lifestyle factors: Nexplanon offers convenience and ease of use, but individual lifestyle factors and preferences may influence contraceptive choices.
- Contraindications: Some medical conditions or medications may contraindicate the use of Nexplanon. It’s important to discuss your medical history and current medications with your healthcare provider before starting Nexplanon.
Overall, Nexplanon can be a suitable contraceptive option for many women of all ages, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine whether it’s the right choice for you based on your individual circumstances and needs.
How soon can I get pregnant after removing Nexplanon?
After removing Nexplanon, fertility typically returns quickly, but the timing can vary from person to person. For most women, ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) resumes within a few weeks to a few months after Nexplanon removal. This means that pregnancy can occur shortly after the implant is removed.
Some women may conceive immediately after Nexplanon removal, while others may take longer to conceive depending on factors such as age, overall health, and individual fertility. It’s important to note that fertility can return before the first menstrual period after Nexplanon removal, so using an alternative form of contraception if you do not wish to become pregnant immediately is recommended.
If you are considering pregnancy after Nexplanon removal, it’s a good idea to track your menstrual cycle and ovulation to help determine the timing of ovulation and optimize your chances of conception. If you have concerns about fertility or difficulty conceiving after Nexplanon removal, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Can Nexplanon be used alongside other forms of contraception?
While Nexplanon is highly effective on its own, it can be used alongside other forms of contraception if desired or if additional protection is needed. Using multiple methods of contraception simultaneously is often referred to as “dual protection” and can offer added reassurance against unintended pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Some combinations of contraception methods may include:
- Condoms: Using condoms in addition to Nexplanon provides dual protection against pregnancy and STIs. Condoms act as a physical barrier that prevents sperm from reaching the egg and also help reduce the risk of STIs by preventing the exchange of bodily fluids.
- Barrier Methods: Other barrier methods, such as diaphragms or cervical caps, can also be used alongside Nexplanon to provide additional contraceptive protection.
- Hormonal Methods: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend combining Nexplanon with other hormonal contraceptive methods, such as birth control pills, patches, or vaginal rings, for added effectiveness or to help manage specific menstrual symptoms.
- Long-Acting Reversible Contraceptives (LARCs): Nexplanon can be used alongside other LARC methods, such as intrauterine devices (IUDs), to provide highly effective contraception for individuals who desire long-term birth control.
It’s important to discuss any plans to use multiple contraceptive methods with a healthcare provider to ensure that they are used correctly and safely. Additionally, using multiple methods may increase contraceptive effectiveness, but it’s essential to consider individual preferences, lifestyle factors, and potential interactions between different contraceptive methods.
Most Common Nexplanon Side Effects
The most common side effects of Nexplanon include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns: This can include irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, or changes in the duration and intensity of menstrual bleeding.
- Headache: Some individuals may experience headaches while using Nexplanon.
- Breast tenderness: Breast tenderness or discomfort may occur as a side effect of Nexplanon.
- Weight gain: While not experienced by everyone, some individuals may notice weight changes while using Nexplanon.
- Acne: Acne or changes in skin condition may occur as a side effect of Nexplanon.
- Mood changes: Some individuals may experience mood swings, irritability, or emotional changes while using Nexplanon.
These side effects are typically mild to moderate in severity and often improve over time as the body adjusts to the presence of the hormone released by Nexplanon. However, if you experience severe or persistent side effects, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Additionally, while rare, Nexplanon may also cause more serious side effects such as blood clots or changes in liver function. If you experience any unusual or concerning symptoms while using Nexplanon, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Long-Term Nexplanon Side Effects
While Nexplanon is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, some individuals may experience long-term side effects. It’s important to note that long-term side effects are less common than short-term side effects and may vary from person to person. Some potential long-term side effects of Nexplanon may include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns: Irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, or changes in the duration and intensity of menstrual bleeding may persist over the long term for some individuals.
- Weight changes: While weight gain is a common side effect of Nexplanon, some individuals may experience long-term changes in weight while using the contraceptive implant.
- Mood changes: Mood swings, irritability, or emotional changes may persist over the long term in some individuals.
- Acne: Acne or changes in skin condition may persist over the long term for some individuals using Nexplanon.
- Decreased libido: Some individuals may experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido over the long term while using Nexplanon.
- Headaches: Headaches or migraines may persist as a long-term side effect of Nexplanon for some individuals.
It’s important to remember that long-term side effects of Nexplanon are typically mild to moderate in severity and may improve over time as the body adjusts to the hormone released by the implant. However, if you experience persistent or severe side effects, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Additionally, while rare, Nexplanon may also cause more serious long-term side effects such as changes in liver function or bone density. If you have any concerns about the long-term effects of Nexplanon, it’s important to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
New and Second Nexplanon Side Effects
While Nexplanon is generally safe and well-tolerated, some individuals may experience new or additional side effects when starting or getting a second Nexplanon implant. These side effects may vary from person to person and can include:
- Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns: Irregular bleeding, spotting between periods, or changes in the duration and intensity of menstrual bleeding may occur when starting Nexplanon or getting a second implant.
- Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches as a new or intensified side effect when using Nexplanon.
- Breast tenderness: Breast tenderness or discomfort may occur as a new or increased side effect when using Nexplanon.
- Weight changes: While weight gain is a common side effect of Nexplanon, some individuals may experience new or additional changes in weight with a new or second implant.
- Mood changes: Mood swings, irritability, or emotional changes may occur as new or increased side effects when using Nexplanon.
- Acne: Acne or changes in skin condition may occur as new or increased side effects when using Nexplanon.
- Decreased libido: Some individuals may experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido as a new or increased side effect when using Nexplanon.
It’s important to remember that side effects of Nexplanon are typically mild to moderate in severity and may improve over time as the body adjusts to the hormone released by the implant. However, if you experience persistent or severe side effects, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Additionally, while rare, Nexplanon may also cause more serious side effects such as changes in liver function or blood clots. If you have any concerns about the side effects of Nexplanon, it’s important to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Side Effects Timeline: Short-Term and Long-Term
Here’s a general timeline for both short-term and long-term side effects of Nexplanon:
Short-Term Side Effects (First Few Months):
- Bleeding Changes: Irregular bleeding, spotting, or changes in menstrual patterns may occur within the first few months of Nexplanon insertion. This is one of the most common short-term side effects.
- Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches, which usually subside over time.
- Breast Tenderness: Breast tenderness or discomfort may occur initially but often resolves within a few weeks.
- Mood Changes: Mood swings, irritability, or emotional changes may occur in the first few months.
- Weight Changes: Weight gain is a common side effect that may manifest in the early stages.
Long-Term Side Effects (Months to Years):
- Persistent Bleeding Changes: Irregular bleeding or changes in menstrual patterns may persist over the long term for some individuals.
- Weight Changes: While weight gain is common in the short term, long-term weight changes may vary.
- Mood Changes: Mood swings or emotional changes may persist over the long term for some individuals.
- Acne: Acne or changes in skin condition may persist over time.
- Decreased Libido: Some individuals may experience a decrease in sexual desire or libido as a long-term side effect.
- Other Effects: Less common long-term side effects such as changes in liver function or bone density may occur, although they are rare.
It’s important to note that individual experiences may vary, and not everyone will experience all of these side effects. Additionally, some side effects may improve or resolve over time as the body adjusts to the hormone released by Nexplanon. If you experience persistent or severe side effects, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Managing Nexplanon Side Effects
Managing Nexplanon side effects involves a combination of strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. Here are some tips for managing common Nexplanon side effects:
-
Bleeding Changes:
- Keep track of your bleeding patterns to monitor changes over time.
- Use menstrual hygiene products, such as pads or tampons, as needed.
- Consider hormonal treatments prescribed by your healthcare provider if bleeding becomes bothersome.
-
Headaches:
- Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help alleviate headaches.
-
Breast Tenderness:
- Wear a supportive bra, especially during physical activity.
- Apply a warm compress to the breasts to relieve discomfort.
- Speak with your healthcare provider if breast tenderness persists or worsens.
-
Mood Changes:
- Engage in regular exercise to promote mental well-being.
- Practice stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga.
- Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional about your feelings.
-
Weight Changes:
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay physically active with regular exercise.
- Focus on overall health and well-being rather than weight fluctuations.
-
Acne:
- Establish a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansers and non-comedogenic moisturizers.
- Avoid touching or picking at acne lesions to prevent scarring.
- Consider over-the-counter or prescription acne treatments recommended by your healthcare provider.
-
Decreased Libido:
- Communicate openly with your partner about changes in sexual desire.
- Explore other forms of intimacy and connection with your partner.
- Speak with your healthcare provider if decreased libido persists or causes distress.
It’s essential to discuss any persistent or bothersome side effects with your healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice, adjust your treatment plan if necessary, or explore alternative contraceptive options. Additionally, if you experience severe or concerning symptoms, seek medical attention promptly.